ceilometer的几个概念
ceilometer 主要有下面几个概念:
- meter 是ceilometer定义的监控项,诸如内存占用,网络IO,磁盘IO等等
- sample 是每个采集时间点上meter对应的值
- statistics 一般是统计学上某个周期内,meter对应的值(平均值之类)
- resource 是被监控的资源对象,这个可以是一台虚拟机,一台物理机或者一块云硬盘
- alarm 是ceilometer的告警机制,你可以通过阈值或者组合条件告警,并设置告警时触发的action
Meter
资源使用的某个计量项,它的属性包括:名称(name)、单位 (unit)、类型 (cumulative:累计值,delta:变化值、gauge:离散或者波动值)以及对应的资源属性等。
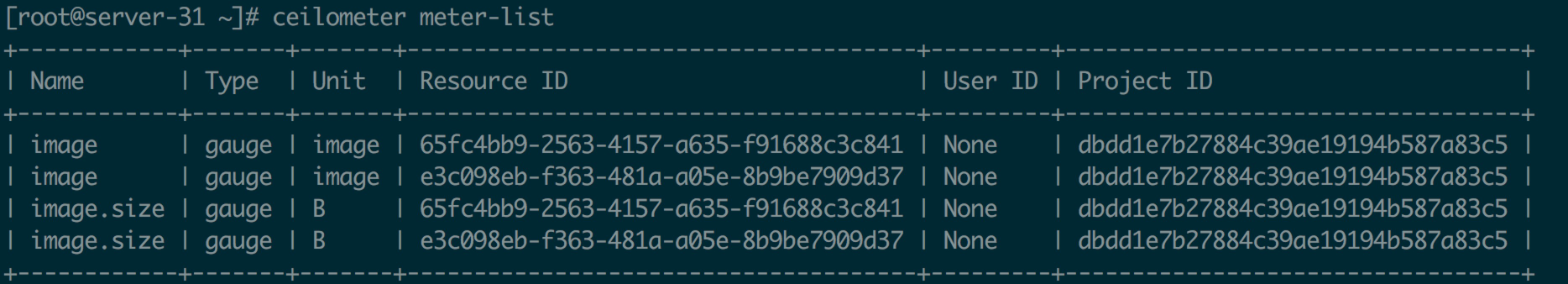
Sample
某时刻某个 resource 的某个 meter 的值。Sample 的收集有区间概念,即收集数据的时间间隔。它的属性出了meter属性外,还有 timestampe(采样时间)和 Volume (采样值)。
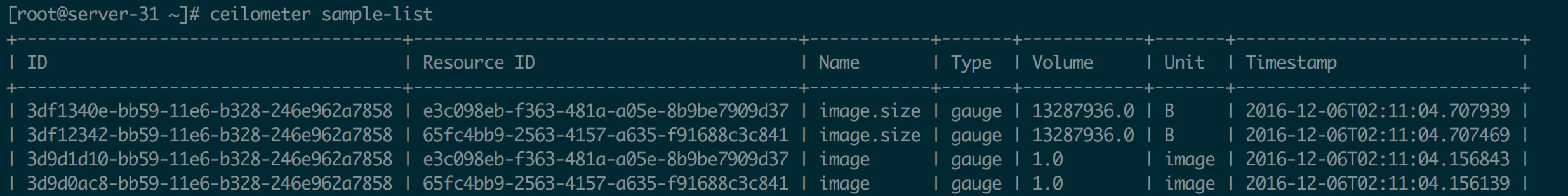
Statistics
一个时间段(Period)内的 samples 聚合值,包括计数(Count)、最大(Max)、最小(Min)、平均 (Avg)、求和(Sum)等。例如:
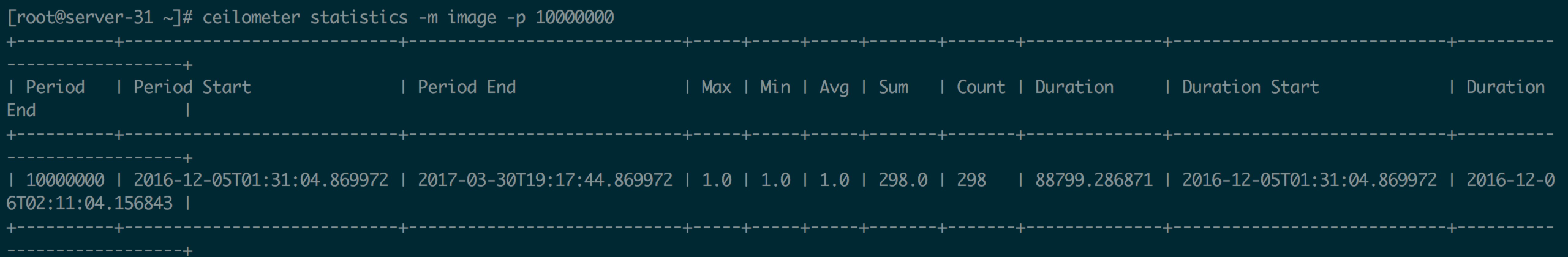
这里的Period表示当前该查询的区间,使用 -p 参数指定
需要注意的是,你可以使用 ”-q“ 指定统计的目标范围。当不指定的时候,表示对当前租户(tenant)内的所有虚机的 sample 做统计。比如指定 resource_id 来只统计某一个虚机:
ceilometer statistics -m cpu_util -p 60 -q resource_id=d7ce68d4-3d58-404c-85a6-f9c19fe9d96c。
ceilometer组成部分
ceilometer组成部分:
1.控制节点。
Central Agent: 调用OpenStack其它组件api采集指标
Notification Agent:接收其它组件主动上报的通知消息
Collector:基于AMQP接收消息,并记录到DataStore
API:运行在管理节点,提供接口访问Data Store
2.计算机点。
Compute Agent:采集本节点性能指标
ceilometer监控项
Ceilometer原生支持的监控指标有很多,考虑到消息服务器和数据库的压力,根据项目需要,只保留需要的指标,其它默认裁剪。同时,扩展了部分指标。
1.虚拟机
- cpu:cpu使用时间
- cpu_util:cpu使用率
- vcpus:使用vcpu数量
- disk.total.size:磁盘总大小
- memory:内存总大小
- memory.usage:内存使用大小
- disk.read.bytes:磁盘读字节数
- disk.read.bytes.rate:磁盘读速率
- disk.write.bytes:磁盘写字节数
- disk.write.bytes.rate:磁盘写速率
- network.incoming.bytes:网络incoming字节数
- network.incoming.bytes:网络incoming字节数
- network.incoming.bytes.rate:网络incoming速率
- network.outgoing.bytes:网络outgoing字节数
- network.outgoing.bytes.rate:网络outgoing速率
2.物理机
- compute.node.cpu.percent:cpu利用率
- compute.node.disk.total:磁盘总大小
- compute.node.disk.used:磁盘使用大小
- compute.node.memory.total:内存总大小
- compute.node.memory.used:内存使用大小
- compute.node.disk.read.bytes:磁盘读字节数
- compute.node.disk.read.bytes.rate:磁盘读速率
- compute.node.disk.write.bytes:磁盘写字节数
- compute.node.disk.write.bytes.rate:磁盘写速率
- compute.node.network.incoming.bytes:网络incoming字节数
- compute.node.network.incoming.bytes.rate:网络incoming速率
- compute.node.network.outgoing.bytes:网络outgoing字节数
- compute.node.network.outgoing.bytes.rate:网络outgoing速率
- compute.node.network.bandwidth:物理网卡带宽
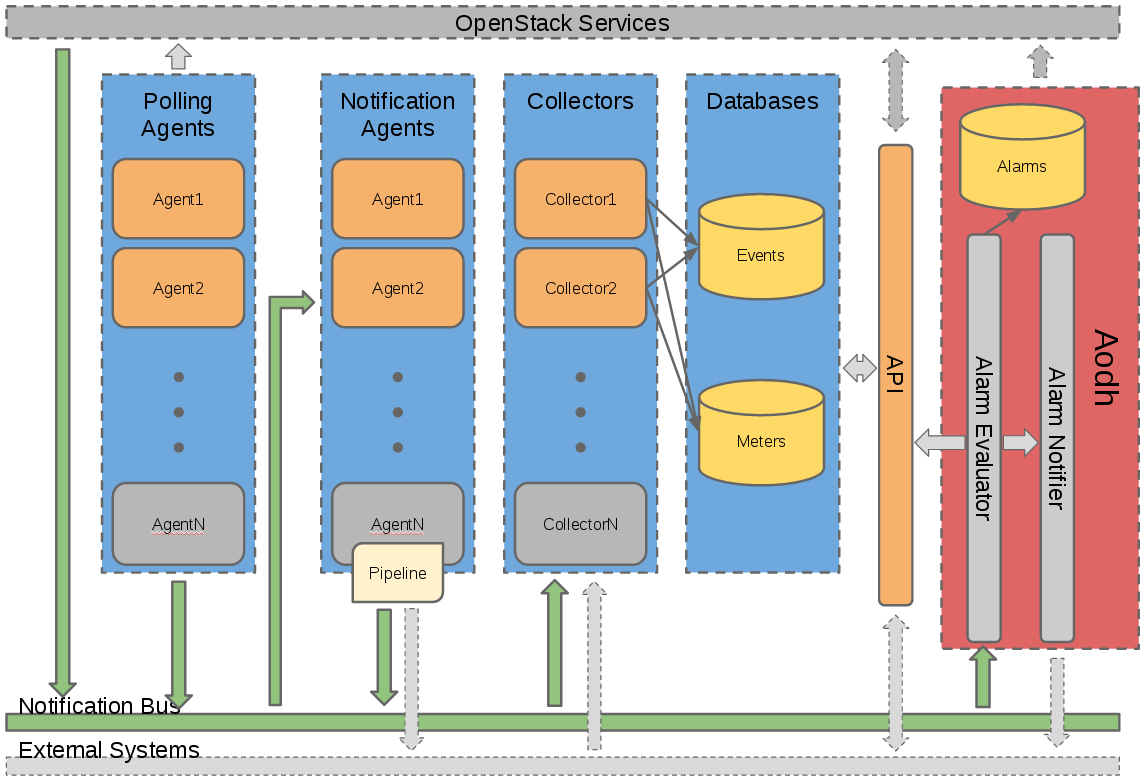
ceilometer收集数据的方式
OpenStack原始数据的收集方式有两种:
一种是通过ceilometer polling agent主动轮询方式,调用相应插件获取性能数据;
另一种是各openstack核心组件主动向消息队列上报自身的性能数据。这两种收集方式都将原始数据发送到消息队列。
ceilometer notification agent监听该消息队列,并将这些原始数据按照一定规则转换成sample和event,再发布到配置的目的端。可配的发布方式包括direct、notifier、udp、kafka和file。
ceilometer collector是可选服务,它从notification消息队列中消费sample和event消息,然后将数据dispatch到配置的目的端:database、file、http、gnocchi,该目的端可以同时配置多项。Ceilometer的逻辑框架如下图所示:
ceilometer监控项
nova
如果想统计虚拟机的一些信息,需要做以下更改:
| 配置项 | 默认值 | 配置项所属group | 配置文件 | 原因 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| instance_usage_audit=True | false | [DEFAULT] | nova.conf | nova默认不会周期性通知所有已知实例的情况,所以如果需要周期获得这些审计信息需要打开它 |
| instance_usage_audit_period=hour | month | [DEFAULT] | nova.conf | 上面开启了周期性通知的信息,这里就是周期性通知的时间间隔 |
| notify_on_state_change=vm_and_task_state | None | [DEFAULT] | nova.conf | 虚拟主机的状态发生变化的时候,nova也会往消息队列里面发送消息,但是需要配置这个配置项 |
| notification_driver=messagingv2 | [] | [DEFAULT] | nova.conf | nova发送notifications信息的驱动 |
因为对CPU的一些特定资源的监控需要在nova里面打开相应的支持,所以需要配置nova的配置文件,设置compute_monitors添加一个ComputeDriverCPUMonitor,如下:
# cat /etc/nova/nova.conf
[DEFAULT]
...
compute_monitors = ["ComputeDriverCPUMonitor","cpu.virt_driver","numa_mem_bw.virt_driver"]
...
# 重启nova-compute服务
# /usr/bin/python /usr/bin/nova-compute
cinder
如果想要获取一些存储的信息,需要做一下更改:
| 配置项 | 默认值 | 配置项所属group | 配置文件 | 原因 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| driver = messagingv2 | [] | [oslo_messaging_notifications] | cinder.conf | cinder发送notifications信息的驱动 |
| control_exchange = cinder | [DEFAULT] | cinder.conf | cinder的messaging的topic |
ceph
根据官方的说明,我们需要进行如下的配置:
...
[client.radosgw.gateway]
rgw enable usage log = true
...
对ceilometer的配置:
配置针对radosgw的access_key和secret_key
[rgw_admin_credentials]
#
# From ceilometer
#
# Access key for Radosgw Admin. (string value)
access_key = <None> # 填入你对应的key
# Secret key for Radosgw Admin. (string value)
secret_key = <None> # 填入你对应的key
Neutron
Havana 版本中添加了收集 Neutron Bandwidth samples的功能。与 Ceilometer 其他采集方式不同的是,bandwidth 的采集是通过 neutron-meter-agent 收集,然后 push 到 oslo-messaging,ceilometer-agent-notification通过监听消息队列来收取bandwidth信息。
其实现是在 L3 router 层次来收集数据,因此需要操作员配置 IP 范围以及设置标签(label)。比如,我们加两个标签,一个表示内部网络流量,另一个表示外部网络流量。每个标签会计量一定IP范围内的流量。然后,每个标签的带宽的测量数据会被发到 MQ,然后被 Ceilometer 收集到。 注意:需要先安装openstack-neutron-metering-agent
yum install -y openstack-neutron-metering-agent
neutron.conf中还需要做一下更改:
[DEFAULT]
service_plugins = metering
重启网络服务: systemctl restart neutron-server
修改/etc/neutron/metering_agent.ini:
[DEFAULT]
# Show debugging output in log (sets DEBUG log level output)
debug = True
driver = neutron.services.metering.drivers.iptables.iptables_driver.IptablesMeteringDriver
# Interval between two metering measures
measure_interval = 30
# Interval between two metering reports
report_interval = 300
interface_driver = neutron.agent.linux.interface.OVSInterfaceDriver
use_namespaces = True
重启网络服务:
systemctl start neutron-metadata-agent
关于neutron配置更为详细信息,参考网站
ceilometer 常用cli命令
获取所有的meters
ceilometer meter-list
查询某种监控资源
ceilometer sample-list -m cpu
查询某个监控资源
ceilometer meter-list --query user=xxxx
查询某种监控资源并且限定条件
ceilometer sample-list --meter cpu -q 'resource_id=921903ea-ccda-4eda-b86e-7d44f3aa71c2;timestamp<2015-1
查询某种资源的统计信息
ceilometer sample-list -m cache.miss
ceilometer statistics --meter cpu_util
查询现在所有的alarm
ceilometer alarm-list
创建一个alarm
ceilometer alarm-threshold-create --name cache --description 'instance running hot' --meter-name cache --threshold 60.0 --comparison-operator gt --statistic avg --period 600 --evaluation-periods 3 --alarm-action 'log://' --query resource_id=INSTANCE_ID
更新某个alarm的阈值
ceilometer alarm-update --threshold 75 -a ALARM_ID
查询某个alarm的历史更改
ceilometer alarm-history -a ALARM_ID
将某个alarm置为无效
ceilometer alarm-update --enabled False -a ALARM_ID
删除一个alarm
ceilometer alarm-delete -a ALARM_ID
得到某个alarm的状态
ceilometer alarm-state-get ALARM_ID
置某个alarm的状态
ceilometer alarm-state-set --state ok(alarm) –a ALARM-ID
查看单个alarm的详细信息
ceilometer alarm-show ALARM-ID
查看单个alarm的状态
ceilometer alarm-state-get -a alarm-id
ceilometer快速安装
puppet-openstack-integration项目可以快速部署openstack all-in-one环境,github链接:puppet-openstack-integration
部署请参考文章: openstack-all-in-one30分钟快速搭建
ceilometer.conf配置
下面是用puppet-openstack-integration 跑出来的 all-in-one环境ceilometer配置如下:
[DEFAULT]
polling_namespaces=central,compute,ipmi
meter_dispatchers=gnocchi
event_dispatchers=gnocchi
http_timeout=600
debug=True
verbose=True
log_dir=/var/log/ceilometer
rpc_backend=rabbit
notification_topics=notifications
[api]
port=8777
host=0.0.0.0
[central]
[collector]
udp_address=0.0.0.0
udp_port=4952
workers=1
batch_size=100
[compute]
[coordination]
[cors]
[cors.subdomain]
[database]
metering_time_to_live=86400
event_time_to_live=86400
connection=mysql+pymysql://ceilometer:ceilometer@127.0.0.1/ceilometer?charset=utf8
metering_connection = mongodb://ceilometer:ceilometer@127.0.0.1:27017/ceilometer
[dispatcher_file]
[dispatcher_gnocchi]
filter_project = services
filter_service_activity = False
resources_definition_file = gnocchi_resources.yaml
[event]
[exchange_control]
[hardware]
[ipmi]
[keystone_authtoken]
auth_uri=http://127.0.0.1:5000/
admin_tenant_name=services
admin_user=ceilometer
admin_password=a_big_secret
identity_uri=http://127.0.0.1:35357/
[matchmaker_redis]
[meter]
[notification]
ack_on_event_error=True
store_events=False
workers=2
[oslo_concurrency]
[oslo_messaging_amqp]
[oslo_messaging_notifications]
[oslo_messaging_rabbit]
rabbit_host=127.0.0.1
rabbit_port=5672
rabbit_hosts=127.0.0.1:5672
rabbit_use_ssl=False
rabbit_userid=ceilometer
rabbit_password=an_even_bigger_secret
rabbit_virtual_host=/
rabbit_ha_queues=False
heartbeat_timeout_threshold=0
heartbeat_rate=2
[oslo_policy]
[polling]
[publisher]
metering_secret=secrete
[publisher_notifier]
[rgw_admin_credentials]
[service_credentials]
auth_type=password
auth_url=http://127.0.0.1:5000/
project_name=services
project_domain_name=Default
username=ceilometer
user_domain_name=Default
password=a_big_secret
[service_types]
[storage]
[vmware]
[xenapi]
参考:
Openstack入门篇-Ceilometer
ceilometer M 版本collector源码分析